public charging
How long does it take to charge your electric vehicle?
Unveiling the EV charging curve
As more drivers make the transition to electric vehicles, many have questions around the EV charging process. How long does it take? What can you expect during your EV charge? What is the EV charging curve? In this blog, we explore the key factors that can impact EV charging duration to help you make the most of your next EV charging session.
Summary:
- Key factors impacting charge time include charger type and EV battery size
- Depending on battery size, an EV may charge up to 80% in 20-30 minutes with a DC charger
- Depending on battery size, an EV may take about 4-15 hours to charge with a Level 2 AC charger
Understanding electric vehicle charging
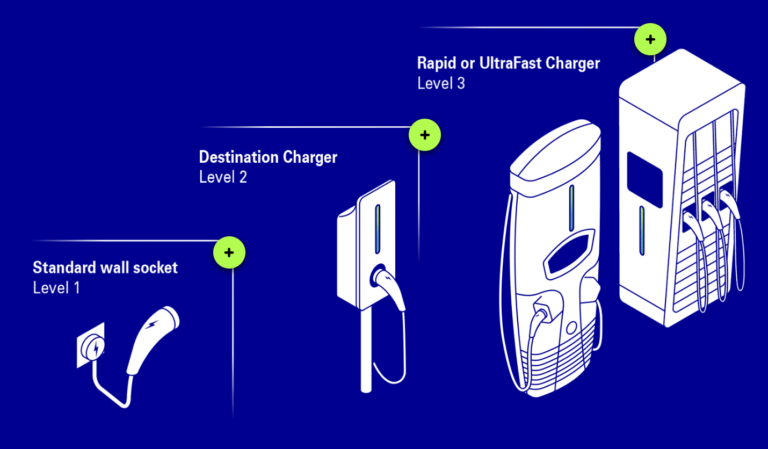
Before diving into charge times, let’s first understand the basics of electric vehicle charging. Electric vehicle charging is typically categorized into three levels:
Level 1 Alternating Current (AC) charging
This is the slowest form of charging and involves plugging the EV into a standard household outlet using the included charging cable. Level 1 charging, typically outputting 1 kW, is convenient for overnight charging at home but is not practical for quickly replenishing battery levels.
Level 2 AC charging
Level 2 charging utilizes a dedicated charging station that delivers higher power levels than a standard household outlet, typically 7-19kW. These charging stations are commonly found in residential garages, workplaces, and public charging stations. Level 2 charging provides faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 and is suitable for daily charging needs.
Level 3 Direct Current (DC) Fast Charging
DC fast charging is the fastest form of EV charging and capable of delivering high power levels to quickly recharge an EV’s battery. These fast chargers, typically outputting 50-350kW are commonly found along highways, major travel routes, and in urban areas, offering convenient charging options for long-distance travel.
Charge times and the charging curve
When discussing charge times for electric vehicles, it’s essential to consider the concept of the charging curve. The charging curve represents the rate at which an EV’s battery charges over time, starting from a low state of charge (SOC) to a high SOC. Understanding the charging curve is crucial for predicting charge times accurately and maximizing the efficiency of the charging process.
Several factors can influence the shape of the charging curve and ultimately impact charge times:
Battery temperature
Battery temperature plays a significant role in determining charging speed and efficiency. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect the performance of lithium-ion batteries and may result in slower charging rates. EVs equipped with battery thermal management systems can mitigate the impact of temperature on charging speed.
State of charge (SOC)
The initial state of charge of the battery, often referred to as SOC, can affect charging speed. EVs tend to charge quicker when the battery is at a lower SOC, such as 20%, and slow down as the SOC increases – known as “tapering”. This is common with Lithium-ion batteries and helps to increase longevity.
Charging power
The power level of the charging station can also influence the speed of a charging session. However, the vehicle’s onboard charger will still affect the speed at which it can use and convert alternating current. The onboard charger is the piece of the EV that converts AC from the power source into DC to charge the battery pack. For example, in a Tesla Model S, the onboard charger is 11.5 kW, so even if you plug into a 19kW AC charger, it will not reach those speeds during your charging session.
Charging dispenser
Different EV manufacturers use various charging dispensers, such as CHAdeMO, CCS (Combined Charging System), and the North American Charging Standard (NACS) commonly found on Teslas. The charging protocol used by an EV can affect compatibility with charging stations and may impact charging speed.
Optimizing charge times
To optimize charge times and make the most of the charging curve, EV owners can follow these tips:
- Plan charging sessions: Before embarking on a long trip, plan charging stops strategically to maximize efficiency and minimize downtime. Utilize charging station locator apps or navigation systems that provide real-time information on charging station availability and amenities.
- Charge during off-peak hours: Take advantage of off-peak electricity rates by scheduling charging sessions during times of low demand. Charging during off-peak hours not only saves money but also reduces strain on the electric grid.
- Monitor battery temperature: Keep an eye on the battery temperature, especially during extreme weather conditions, to ensure optimal charging performance. Preconditioning the battery before charging in hot or cold temperatures can help maintain efficiency and prolong battery life.
- Consider fast charging: For long-distance travel or time-sensitive situations, consider utilizing DC fast charging stations to minimize charge times. Fast chargers can provide a significant boost in charging speed, allowing you to quickly get back on the road.
Electric vehicle charging is a dynamic process influenced by various factors, including battery temperature, state of charge, charging power, and charging protocol. Understanding the charging curve is essential for accurately predicting charge times and optimizing the charging process. By following best practices, EV owners can enjoy convenient and efficient charging experiences while embracing the benefits of clean and sustainable transportation.
Go further
Find bp pulse public charging locations
We’re working to build out fast, reliable chargers in accessible locations across the country. Whether you’re commuting to work or driving coast to coast, we’re developing a national network that’s designed for you.
Date
25 June 2024
author

Ross O'Brien
Director of Operations
bp pulse Americas
Topics